There’s been much talk about Trump’s plan for jobs and infrastructure that entails over one trillion dollars in new spending (without tax increases) and promises to employ thousands of American workers. Because it looks like this would require significant deficit spending, it has drawn stiff criticism: even Trump’s the own conservative supporters have expressed concern.
Among advocates of Keynesian spending and Modern Money Theory (MMT), however, some precautionary excitement can be observed. Their perspective is different because they are unafraid of a government deficit, and in favor of direct job creation. They understand that deficit-spending is not inherently bad, and that the US government will never have to default on its debt. When the economy is not at full employment, increasing the deficit would actually be helpful, not harmful.
A fiscal stimulus aimed at reducing unemployment is timely and necessary. Despite the confidence expressed by the Fed about the latest employment numbers, the situation for those who are jobless is not looking good. One of the reasons for the latest rate hike by the Fed was their positive outlook on unemployment numbers. Chairman Yellen has gone as far as saying that (at 4.6% unemployment rate) we are close to full employment and fiscal stimulus is not necessary to reach that goal.
However, the low official joblessness rate hides the fact that an increasing number of Americans have left the labor force altogether; for example there are currently over 5 million Americans who are not in the labor force but have reported that they want a job. This is where a Job Guarantee program could come in handy. In short, the government would act as an Employer of Last Resort, effectively guaranteeing a job to all of those willing and able to work.
And if Trump uses the deficit-spending towards jobs in infrastructure, it might result in something that resembles the job guarantee policy that America needs**. I argue, however, that the financial feasibility should not be the only criterium for a successful implementation of the job-guarantee. It also has to be sustainable. If we’re going to be at full employment, we have to do it in a way the planet can handle.
The current structure of the economy relies too heavily on fossil fuels, wasteful production methods and non-renewable resources. Unless we change this, sustaining full-employment would result in increasing production, consumption, and waste. My favorite Keynes’ quote is that “In the long run we are all dead.” If we’re talking about a long run of increasing pollution, he will surely be right. As we know, too much of a good thing can be a bad thing. This applies to jobs too. Unless they are green jobs, too many jobs will be bring us environmental destruction.
The issue of the environmental sustainability of a Job Guarantee program has been on my mind since I first heard of the proposal. Mathew Forstater’s Green Jobs proposal was inspirational to my work. In my Master’s thesis, I tweak its existing framework to target environmentally sustainable outcomes. I find that we can transform the Job Guarantee program to ensure its sustainability without increasing its cost. Here’s how:
I set up the program in a way that promotes social enterprise and community development, following the work of Pavlina Tcherneva et al. With the help of social entrepreneurs, NGOs, and Nonprofit Organizations, local communities should decide what projects will be undertaken. For example, communities along the Hudson river could support a program where workers dealt with invasive species such as the zebra mussel and water chestnut. Other localities could handle neighborhood farming, recycling centers, flood containment structures, bike paths, etc.. It’s been found that if the community is involved in determining what projects are taken on, participation levels are higher.
A more detailed account of my proposal and calculations is available upon request, but this is the gist of it: I used an Input-Output model to establish what would be the cost of employing the official U-3 unemployed population into “green” Job Guarantee jobs. That framework accounts for indirect job creation related to the proposal, but not induced employment. What I find is that the US government can, under conservative assumptions, employ all of those who are officially unemployed for around 1.1% of GDP while paying them a $15hr wage. That is about 17% of the annual military budget. The Green Job Guarantee program is projected to cost just under 200 Billion dollars per year in order to ensure employment for 7.8 million people.
As the world economy quickly transitions into a more sustainable state, a shift in the productive structure will occur, rendering some current occupations useless. Workers who are employed in areas like fossil fuel energy generation (the fabled coal workers of the American Midwest for example) will be left without a job and unlikely to find a new one right away. There is no way to predict how quickly this transition will occur: it could be a gradual–albeit fast–process if led by government initiative, a slower and insufficient movement if guided by profit motives, or even a sudden transition caused by widespread popular response to natural disasters.
Given current trends it is safe to assume that the transition to a renewable energy generation and a sustainable economy will occur before the fossil reserves are depleted. Just as the stone age ended before we ran out of stone, the “oil-age” will end before we run out of oil. As such, fossil fuel workers (and those who depend on their consumption) are at risk of losing their jobs in the near future. A Job Guarantee program would allow those workers to not only find employment readily, but also to acquire the on-the-job skills that will allow them an easier transition into the Green economy.
So as we continue to criticize and investigate the means of job-creation proposed by the President-Elect, let’s look beyond the government deficit, and consider the planet, too. Whether you’re afraid of government debt or not, you should be concerned with the destruction of the earth. If we are going to have a public program that aims a generating new jobs and bringing people back into the workforce, then that program should be a Job Guarantee. But, if we’re going to guarantee jobs, the will have to be green. And we have all the tools we need to make that happen.
*Interested in some good work on how to build a sustainable economy? Check out the publications from PERI and the Binzagr Institute for Sustainable Prosperity. Interested in a non-profit that is already doing some great things in that area? Visit GreenWave‘s website and get involved!
** I must make clear that, although Trump’s infrastructure plan might very loosely look like a Job Guarantee program because of its intent, it differs significantly from it because of how it will will be implemented. The president elect’s plan is based on private spending and making concessions to big corporations; it is basically a big giveaway to developers and not a program to ensure full-employment and financial stability.





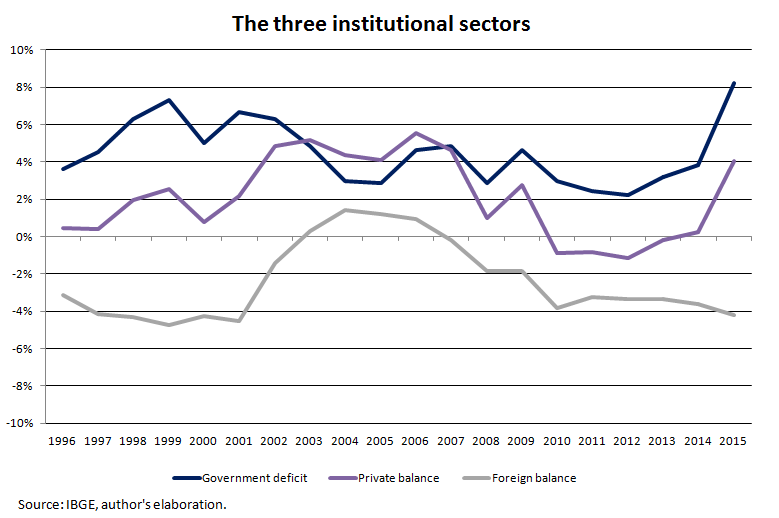
 International conditions also played a major role in boosting the domestic economy. High international liquidity and the commodity-price super cycle guaranteed appreciation of the exchange rate, which beyond positively impacting domestic real wages, also helped to keep inflationary pressures under control by making foreign goods more accessible.
International conditions also played a major role in boosting the domestic economy. High international liquidity and the commodity-price super cycle guaranteed appreciation of the exchange rate, which beyond positively impacting domestic real wages, also helped to keep inflationary pressures under control by making foreign goods more accessible.